The human body is an example of marvelous engineering, as all of our systems are so intrinsically connected and interplay in ways we are only beginning to understand. The gut-brain axis is a prime example of this intricate connection, highlighting how the health of our gut can have varying effects on both our mental and physical well-being.
From ancient times, we have emphasized the importance of gut health. The saying “what you eat, you become” rings true, as the nutrients we absorb from our food nourish our cells and influence our genes. Some recent research has added more depth to this understanding, showing how the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating our immune system and even impacting our mood and cognitive function.
What is Gut Microbiome?
The gut microbiome refers to the trillions of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that live in our digestive tract. These microorganisms play a vital role in digesting food, producing essential nutrients, and protecting against harmful pathogens.
The gut microbiome is also referred to as our second brain, as it influences a wide range of physiological processes, including digestion, immunity, and even mood regulation. The foods we consume, the lifestyle we lead, and the stress we experience can significantly impact the composition of our gut bacteria, thereby affecting our overall health.
Decoding the Gut-Brain Axis: How Are Gut and Brain Connected?
The gut-brain axis is a complex bidirectional communication network that connects the gastrointestinal tract to the central nervous system. This intricate relationship is facilitated by a variety of mechanisms, including the vagus nerve, the immune system, and the endocrine system.
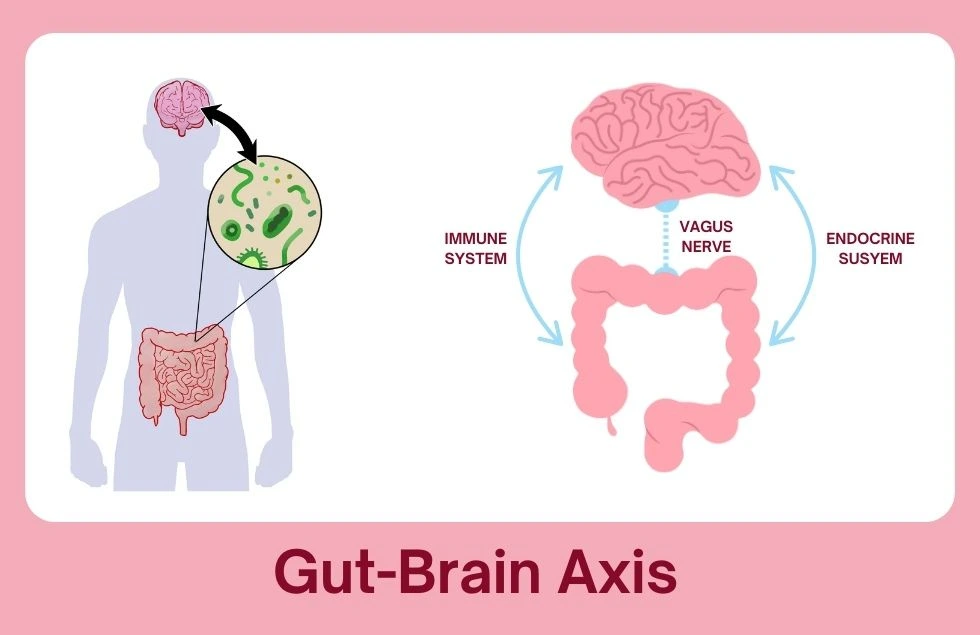
The Vagus Nerve: The Body’s Information Superhighway
The vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve in the body, plays a crucial role in transmitting signals between the gut and the brain. It carries sensory information from the gut to the brain, such as feelings of fullness or discomfort. Additionally, it sends signals from the brain to the gut, influencing digestive processes and regulating gut motility.
The Immune System: A Gut-Brain Connection
The gut is home to a significant portion of the body’s immune system. The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is responsible for recognizing and responding to harmful pathogens. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can lead to chronic inflammation, which has been linked to various health conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and even neurodegenerative disorders.
The Endocrine System: Hormonal Harmony
The gut and the brain communicate through a variety of hormones, including serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in regulating mood, anxiety, and sleep. Disruptions in the gut microbiota can affect the production of these hormones, leading to imbalances in mood and behavior.
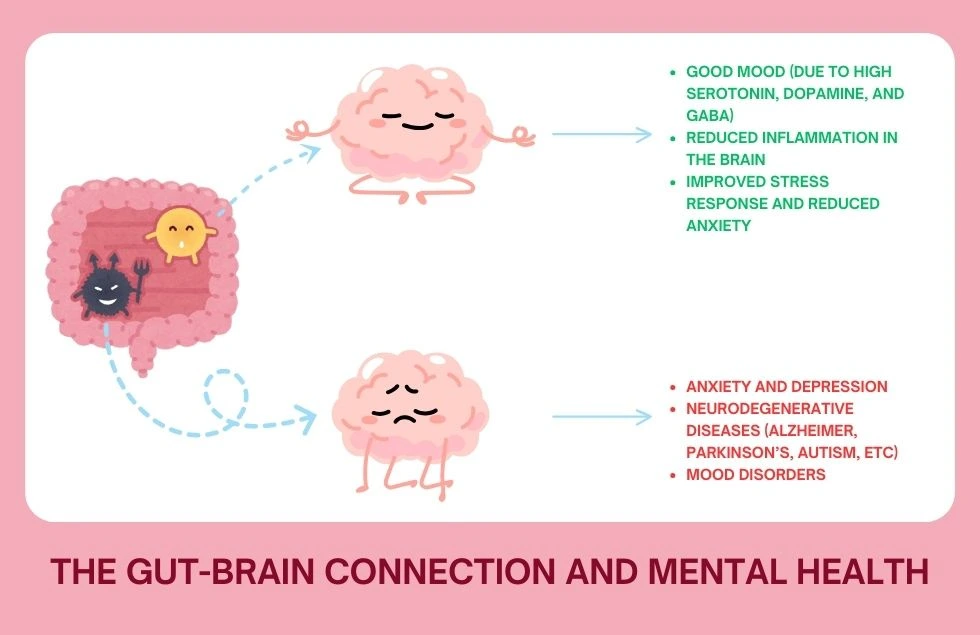
The Gut-Brain Connection and Mental Health
The intricate nature of the microbiota gut brain axis has far-reaching implications for mental health. Emerging research suggests that imbalances in the gut microbiome can contribute to the development of various mental health disorders.
 Source: Freepik
Source: Freepik
Anxiety and Depression
The gut-brain axis plays a significant role in regulating mood and emotions. Studies have shown that individuals with anxiety and depression often exhibit altered gut microbiota composition. Furthermore, probiotics and dietary interventions have been shown to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression by modulating gut microbiota and neurotransmitter levels.
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are characterized by progressive neuronal loss. A recent study published in MDPI has suggested a bidirectional communication between the gut microbiota and the brain, highlighting its role in various neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s, autism, and Parkinson’s. Their suggests that gut dysbiosis may contribute to the development and progression of these diseases. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and neurotoxic compounds produced by harmful gut bacteria may contribute to neuronal damage and cognitive decline.
Mood Disorders
The gut microbiome can influence mood disorders like bipolar disorder and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Imbalances in gut microbiota can disrupt the production of neurotransmitters, leading to mood swings, irritability, and fatigue. By restoring gut health, individuals may experience improved mood regulation and reduced symptoms of these disorders.
The Gut-Brain Connection and Physical Health
1.Digestive Disorders
The gut microbiome plays a significant role in maintaining digestive health. Imbalances in gut microbiota can lead to various digestive disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and celiac disease. By restoring a healthy gut microbiome, individuals may experience relief from digestive symptoms and improved quality of life.
2.Immune Function
As already mentioned, gut is also referred to as the “immune system’s second brain.” The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) houses a significant portion of the body’s immune cells. A healthy gut microbiome helps to maintain a strong immune system by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful pathogens.
3.Metabolic Health
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), produced by gut bacteria, have been shown to influence insulin sensitivity, glucose metabolism, and body weight. Imbalances in gut microbiota can contribute to metabolic disorders such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
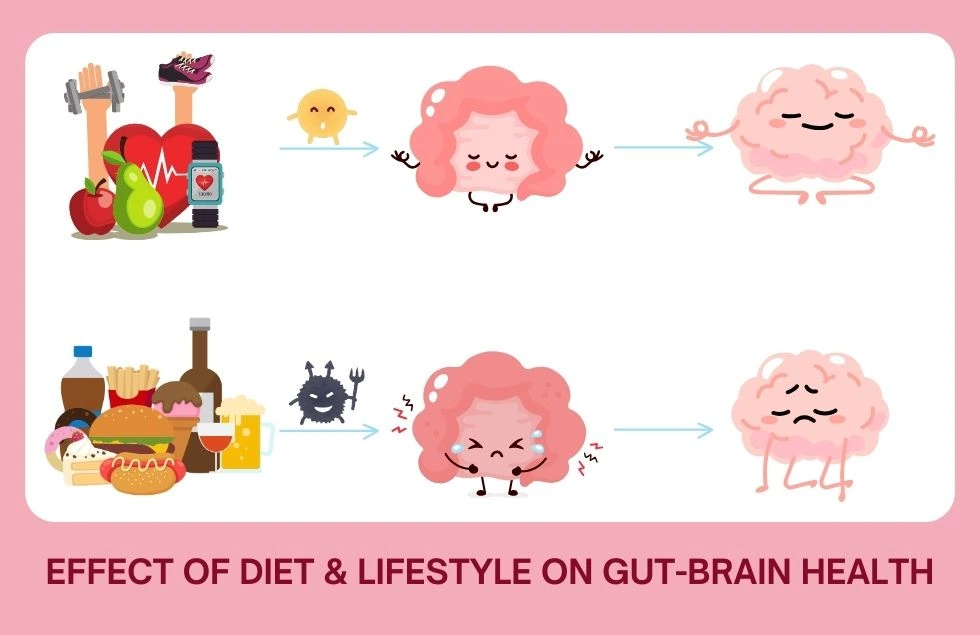
Improving Gut Health: Practical Tips
Diet: Fueling Your Gut
A balanced diet is the cornerstone of good gut health. It’s essential to consume a variety of foods rich in fiber, prebiotics and probiotics, and fermented foods. Dietary fiber intake acts as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Probiotics, found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods, introduce live bacteria to your digestive system, promoting a healthy balance.
Specific nutrients play crucial roles in gut health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and flaxseed, have anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe the gut lining. Vitamin D, often obtained from sunlight or supplements, is linked to improved gut barrier function. Zinc, a mineral essential for immune function, can also positively impact gut health.
Also Read: The Power of Sustainable Eating: How Your Food Choices Are Saving Our Planet
Lifestyle Factors: A Holistic Approach
Your lifestyle significantly influences your gut health. Chronic stress can disrupt the gut-brain axis, leading to digestive issues. Effective stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help alleviate stress and improve gut function.
Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health, including gut health. During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates tissues, including those in the digestive tract. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Regular physical activity stimulates digestion, promotes bowel regularity, and reduces inflammation. Incorporate both aerobic exercises like walking or running and strength training into your routine.
Intermittent fasting is also an amazing way to improve your gut health. The 16 hour fasting period give the digestive system time to rest and repair, potentially enhancing gut barrier function and overall digestive health.
The Impact of Alcohol and Smoking
Alcohol and smoking can have detrimental effects on gut health. Excessive alcohol consumption can irritate the gut lining, leading to inflammation and increased permeability. Smoking can damage the gut lining, impair nutrient absorption, and increase the risk of various digestive disorders.
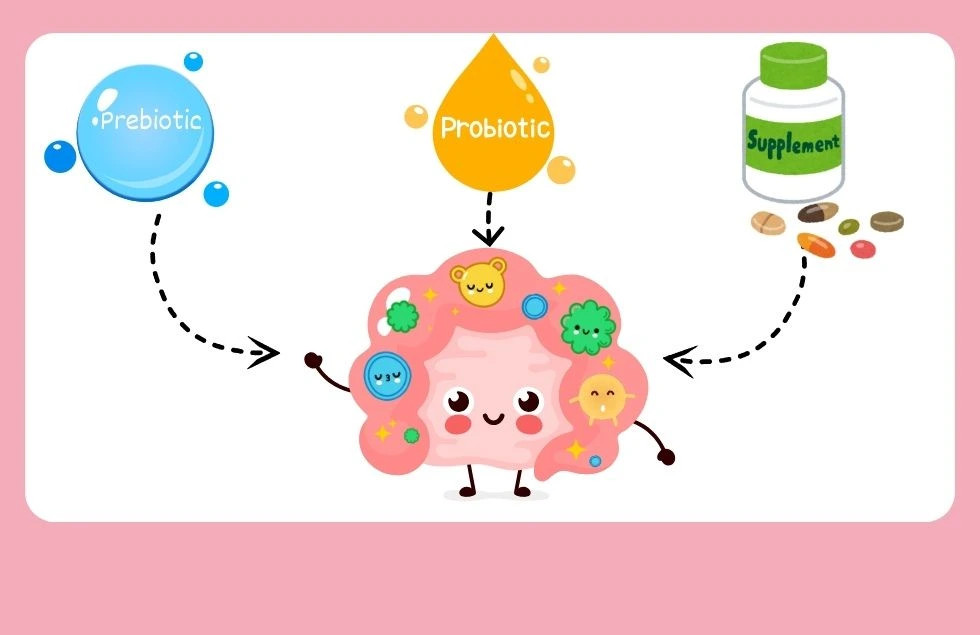
Probiotics and Supplements
Probiotic supplements can introduce beneficial bacteria into your gut and improve gut health, especially when your diet lacks sufficient probiotic-rich foods. However, it’s important to choose reputable brands and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
 Source: Freepik
Source: Freepik
Prebiotics, like fiber, feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut, promoting their growth and activity. They are found naturally in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas.
Prebiotics vs. Probiotics: A Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Prebiotics | Probiotics |
| Definition | Non-digestible food ingredients that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. | Live beneficial bacteria that are consumed through fermented foods or supplements. |
| Sources | Garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, leeks, whole grains. | Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, tempeh. |
| Function | Feed and stimulate the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. | Add beneficial bacteria to the gut microbiome. |
| Benefits | Improve digestion, enhance immune function, and may reduce the risk of certain diseases. | Improve gut health, boost immune system, and may help with conditions like diarrhea and irritable bowel syndrome. |
| Mechanism | Serve as food for probiotics and other beneficial bacteria. | Colonize the gut and help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. |
| Usage | Often added to foods or taken as supplements. | Consumed through fermented foods or as dietary supplements. |
Nurturing Your Inner Ecosystem
The gut-brain axis is a testament to the intricate connection between our mind and body. By understanding this complex relationship, we can take proactive steps to nourish our gut microbiome and promote overall well-being. From dietary choices to lifestyle habits, every aspect of our lives can impact the health of our gut. By making conscious choices and prioritizing gut health, we can unlock the full potential of this remarkable connection and live a healthier, happier life.
For more such health tips and wellness advice, check out our other blogs and articles at Stay Fit Stay Healthy. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing valuable information on how to optimize your health and well-being through simple, practical strategies. Start your fitness journey today!

